[React] The Component lifecycle(ver 16.3 ~)
React에서 사용되는 Component lifecycle method의 종류와 사용처를 정리하고자 한다. 비록 16.8 버전 이후 Hook 기능의 추가로 인해 Class Component의 사용량은 떨어질 것이라 생각되지만 정리에 의의를 두자.
Lifecycle Methods Diagram
각각의 lifecycle method들을 설명하기 전에 먼저 전체 다이어 그램을 통해 구조를 설명하고자 한다. lifecycle은 크게 Mounting, Updating, Unmounting으로 구분되며 각 항목에는 여러개의 method가 존재한다.
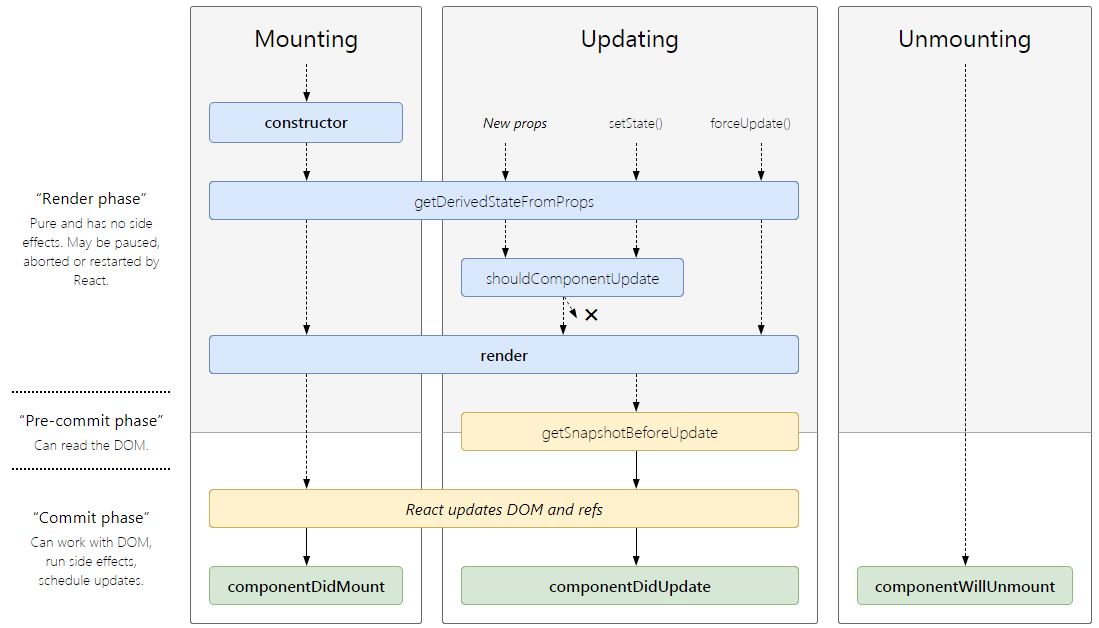 React lifecycle moethods diagram
React lifecycle moethods diagram
Mounting
Updating
static getDerivedStateFromProps()shouldComponentUpdate()render()getSnapshotBeforeUpdate()componentDidUpdate()
Unmounting
render()
render()
render()는 this.props와 this.state 값을 검증하며, 반환값을 화면에 랜더링시킨다. 반환값의 종류로는 React elements, 배열, Portals, 문자열, 숫자, boolean, null이 있다.
render() 내부에서 this.state값을 변경하면 무한 업데이트가 일어날 수 있으므로, 순수함수로 작성되어야 한다.
render() 사용 예시
render() {
return (
<div>
<SomeComponent />
<OtherComponent />
</div>
)
}
constructor()
constructor(props)
constructor는 다음 두 가지 목적을 위해 주로 사용된다.
- 컴포넌트의
state초기값을 정의한다(this.state = {...}형태로 사용됨). - 컴포넌트에서 사용되는 이벤트 핸들러를 바인딩 한다(
this.someEventHandler = this.someEventHandler.bind(this)형태로 사용됨).
constructor() 사용 예시
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
color: 'red',
};
this.eventHandler = this.eventHandler.bind(this);
}
componentDidMount()
componentDidMount()
componentDidMount()는 컴포넌트가 최초로 마운팅 된 이후 1회 실행된다. 다음과 같은 목적을 위해 주로 사용된다.
- 이벤트 리스너 등록 및 ajax 처리
setTimeout,setInterval실행
componentDidMount() 내부에서 this.setState()를 실행 할 경우 추가적인 랜더링이 발생하지만, 브라우저가 화면을 갱신하기 이전에 수행된다. 때문에 state의 초기값 지정은 constructor() 내부에서 처리하는 것을 권장한다.
componentDidMount() 사용 예시
componentDidMount() {
this.fetchSomeData();
}
shouldComponentUpdate()
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState)
shouldComponentUpdate()는 this.state나 this.props값에 변경이 있을 때 실행된다. true값을 리턴하면 render() 메서드가 실행되며 false를 리턴하면 업데이트가 무시된다. 때문에 해당 메서드는 불필요한 랜더링을 방지하여 성능 최적화를 위해 주로 사용된다.
기본 반환값은 true이기 때문에 필요한 조건에 맞추어 false를 린턴 시켜주면 된다.
shouldComponentUpdate() 사용 예시
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
return nextProps.foo !== this.props.foo;
}
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate()
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState)
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate()은 render()가 실행되고 실제 DOM에 변경사항이 반영되기 직전에 실행된다. 이 메서드에서 반환한 값은 componentDidUpdate()의 3번째 인자로 사용된다. 주로 DOM에 대한 정보를 capture 할 때 사용된다(ex. scroll position).
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate() 사용 예시
아래는 공식 홈페이지에서 발췌한 예시로, 목록이 늘어나도 scroll의 위치를 고정시키기 위해 사용되었다.
class ScrollingList extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.listRef = React.createRef();
}
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps, prevState) {
if (prevProps.list.length < this.props.list.length) {
const list = this.listRef.current;
return list.scrollHeight - list.scrollTop;
}
return null;
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) {
if (snapshot !== null) {
const list = this.listRef.current;
list.scrollTop = list.scrollHeight - snapshot;
}
}
render() {
return (
<div ref={this.listRef}>{/* ...contents... */}</div>
);
}
}
componentDidUpdate()
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot)
componentDidUpdate()는 컴포넌트가 업데이트 된 이후 실행되며, 초기 mounting 이후에는 실행되지 않는다. componentDidUpdate()는 다음 목적으로 주로 사용된다.
- 컴포넌트의 업데이트 이후 DOM 조작
- API 호출 등 네트워크 요청
componentDidUpdate() 내부에서 this.setState()를 호출할 때에는 항상 조건문으로 감싸주어야 한다. 그렇지 않으면 무한 업데이트가 발생하게 된다.
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate()에서 반환한 값을 3번째 인자로 활용 할 수 있다. 기본값은 undefined이다.
componentDidUpdate() 사용 예시
componentDidUpdate(prevProps) {
if (this.props.userID !== prevProps.userID) {
this.fetchData(this.props.userID);
}
}
static getDerivedStateFromProps()
static getDerivedStateFromProps(props, state)
getDerivedStateFromProps()는 prop으로 전달받은 값을 state로 동기화 하고 싶을 때 사용된다. null을 리턴하면 동기화가 일어나지 않는다.
다만, React 공식 홈페이지에서는 getDerivedStateFromProps()를 제한적으로 사용할 것을 권장하고 있다. 자세한 내용은 링크를 참고하자.
static getDerivedStateFromProps() 사용 예시
getDerivedStateFromProps(props) {
return {
value: props.foo,
};
}
componentWillUnmount
componentWillUnmount()
componentWillUnmount는 컴포넌트가 unmount 되기 직전에 실행된다. 주로 componentDidMount()에서 등록한 이벤트 리스너, setInterval, setTimeout을 클리어 하거나 외부 라이브러리 인스턴스 제거 등에 사용된다.
componentWillUnmount 사용 예시
componentWillUnmount() {
this.removeEventListener();
}

Comments